Documentation Overview
Welcome to the CodeLogician documentation. Here you'll find comprehensive guides and documentation to help you start working with CodeLogician as quickly as possible.
What is CodeLogician?
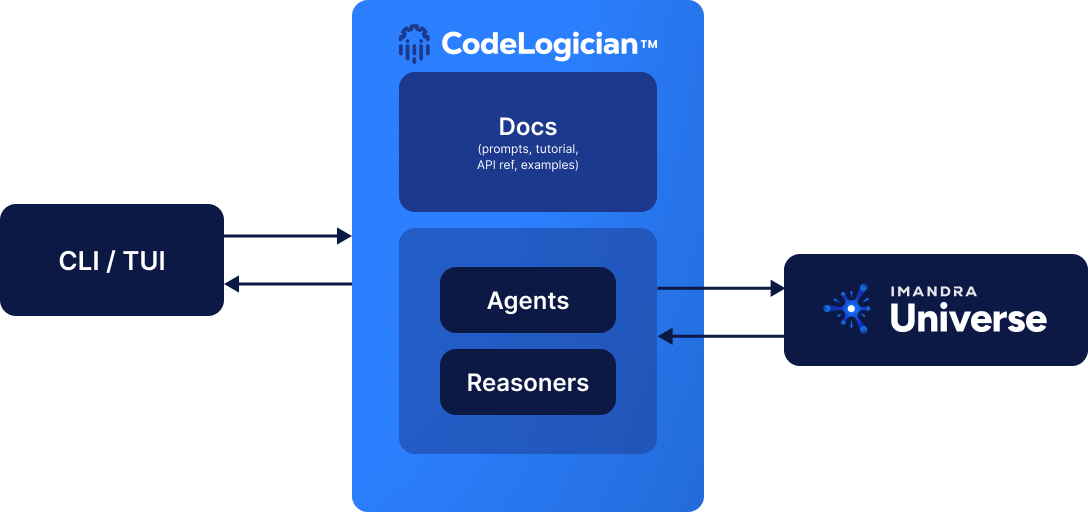
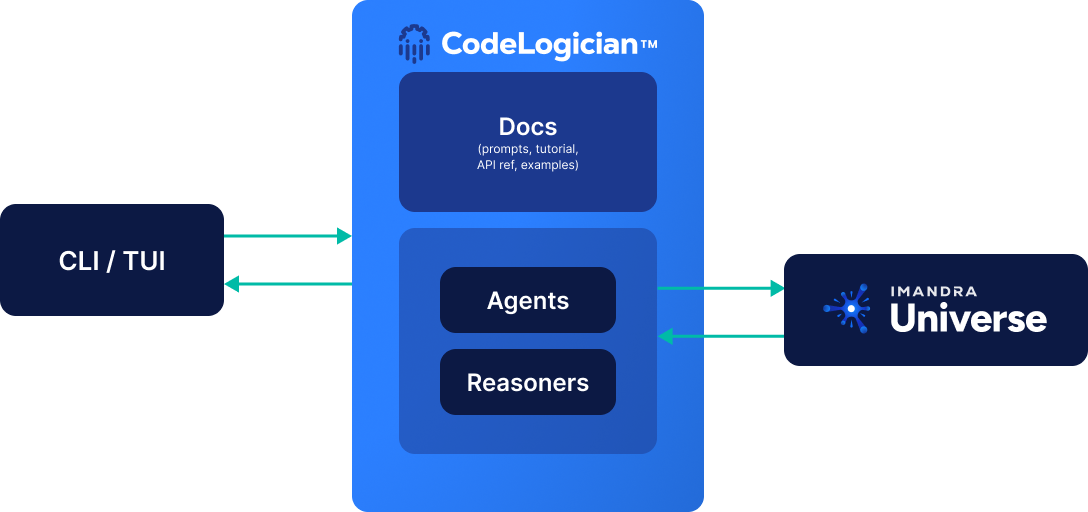
CodeLogician is a neurosymbolic, agentic governance platform that brings mathematical reasoning to AI-assisted software development. Its initial focus is on providing access to ImandraX, together with an agent that automatically formalizes source code into logic and uses Imandra's reasoning engine to produce proofs, counterexamples, and exhaustive analyses of code behavior. CodeLogician serves as the source of mathematical ground truth, ensuring that software behaves as intended with certainty rather than probability.
CodeLogician does not compete with LLM-based coding tools such as ChatGPT, Gemini, or Grok; instead, it augments and guides them. Through a CLI interface, LLM-based tools can invoke CodeLogician's reasoning capabilities and learn—via structured feedback—how to formalize code more effectively over time. While the first release centers on ImandraX, CodeLogician is designed as a multi-reasoner platform, with additional engines (such as TLA+) hosted within Imandra Universe and exposed through the same governance and orchestration layer.


It helps your coding agent think logically about the code it's producing and test cases it's generating. The fundamental flaw that all LLM-powered assistants have is the reasoning they're capable of is based on statistics, while you need rigorous logic-based automated reasoning.
- Generated code is based on explainable logic, not pure statistics
- Generated test cases come with quantitative coverage metrics
- Generated code is consistent with the best security practices leveraging formal verification
Where should I use CL?
CodeLogician can, in principle, be applied to reasoning tasks across the entire software stack—from high-level architecture down to low-level implementation concerns. However, its primary strength lies above the level of individual lines of code, where behavior emerges from the interaction of components, systems, and requirements rather than from isolated constructs.
In particular, CodeLogician excels at architectural design reasoning, multi-system integration analysis, and functional requirements validation. These domains benefit most from CodeLogician's ability to translate code and specifications into formal models, orchestrate multiple reasoning engines, and reason exhaustively about system-level behavior, invariants, and interactions. This is where traditional tools struggle: architectural intent is informal, integrations explode combinatorially, and requirements are rarely checked with mathematical completeness.
By contrast, low-level application-specific issues (such as SQL injection or memory safety) and hardware-adjacent concerns (such as C++ memory allocation) are already well served by specialized static analyzers, linters, and runtime tools optimized for those domains. While CodeLogician can reason about these layers, its unique value is not in replacing mature point solutions, but in governing how systems are designed, integrated, and validated against their intended behavior—with proofs, not heuristics.
| Reasoning domains | Examples | Software Abstraction High | CodeLogician applicability |
|---|---|---|---|
Architectural designs | SysML v2 modeling, verification and testing | ||
Multi-system integration testing | Integration testing | ||
Functional requirements | Requirements modeling and functional testing | ||
Low-level application-specific | SQL injection issues | ||
Hardware-related concerns | Memory allocation in C++ | ||
Low | |||
Getting Started
To run CodeLogician, please obtain an Imandra Universe API key
available (there's a free starting plan) at https://universe.imandra.ai
and make sure it's available in your environment as IMANDRA_UNI_KEY.
Three typical workflows:
- Direct mode - invoke reasoners and agents directory from the command line:
- Learn how to use IML/ImandraX via
doccommand (e.g.codelogician doc --help) - Synthesizes IML from source code and uses the
evalcommand to evaluate it - If there are errors, use
codelogician doc view errorscommand to study how to correct the errors and re-evalute the code
- BYOA mode - CodeLogician Agent is a LangGraph-based agent for automatically formalizing source code.
- With
agentcommand you can formalize a single source code file (e.g.codelogician agent PATH_TO_FILE) - With
multiagentcommand you can formalize a whole directory (e.g.codelogician agent PATH_TO_DIR)
- Server - this is a "live" and interactive version of the
multiagentcommand, but one you can interact with and one that "listens" to live updates and automatically updates formalization as necessary. You can start the server and connect to it with the TUI (we recommend separate terminal screens).
Getting Started
New to CodeLogician? Start here:
- Get your Imandra Universe API key - Free tier available
- Getting Started - Learn the basics and get up and running
Tutorials
Learn how to use CodeLogician with step-by-step guides:
- CLI Tutorial - Get started with CodeLogician CLI
- TUI Tutorial - Using the Terminal User Interface
Real-World Examples
Learn from production use cases that demonstrate CodeLogician's capabilities:
- Case Studies - Real-world applications across different domains
- Algorithmic Trading Rules - Detecting redundant rules in financial systems
- LSE Trading Systems - MIT201 compliance verification
- View workflow diagrams and formal verification results